Thông tin sản phẩm
Содержание
At maturity level 4 Sub-processes are selected that significantly contribute to overall process performance. These selected sub-processes are controlled using statistical and other quantitative techniques. An Axelos endorsement is available for each assessment and provides an independent verification of the rating achieved. This acts as a formal confirmation of the organization’s ability to perform as an effective service provider and supports organizations in differentiating themselves for bids and request for proposal responses. With EPM and BI integrating, reaching this ultimate goal becomes a distinct possibility for many organizations. But maturing to the level of predictive analytics does require several different and sometimes complex steps.
- The Capability Maturity Model was originally developed as a tool for objectively assessing the ability of government contractors’ processes to implement a contracted software project.
- You should not wait until implementing ITIL 4 before having an assessment.
- Digital health interventions are targeted to health workers to give them immediate access to improve decision support mechanisms / telemedicine.
- Department of Defense in evaluating the capability of software contractors as part of awarding contracts.
- The data regulation and management guidelines are defined as better and start integrating with the company processes.
- Strong Level 2 managers acknowledge that they don’t know what they don’t know.
So, our software engineers have saved $3,023,064 on their very first implementation of a CMMI®-compliant software project. It is not a complete map, just a representative portion of the entire piece. 3.Supplier appraisal—This appraisal is identical continuous delivery maturity model to the progress appraisal, except that no employees of the enterprise examined are members of the appraisal team. Will describe how the estimation process in the Data Vault 2.0 methodology is based on the comparison of estimated and actual effort.
Software Quality management – Management can effectively control the software development effort using precise measurements. At this level, organization set a quantitative quality goal for both software process and software maintenance. At this stage, all the projects follow the data governance guidelines and principles. Data models are documented and made available throughout the organization. The Capability Maturity Model was originally developed as a tool for objectively assessing the ability of government contractors’ processes to implement a contracted software project. The model is based on the process maturity framework first described in IEEE Software and, later, in the 1989 book Managing the Software Process by Watts Humphrey.
Process Maturity Levels
Get an idea of your organization’s UX maturity by taking a short quiz . She conducts research and leads training seminars to help digital product teams expand and improve their UX practice. Her research findings and recommendations are informed by her background in information theory and design, as well as her development experience. Organizations at this maturity level have invested in contributing back to industry standards and rely on user research to drive new investments and markets. The processes and staff may be high-quality and consistent, but the organization may get too focused on process instead of outcome and effects or the leaders may be focused on metrics that are not user-centered.
KM is foundational to an intelligent and connected workforce-including the customers and partners that workforce exists to serve. Finally, your KM tools and technology enter the strategic phase once you begin considering KM through the lens of infrastructure. How can we invest in infrastructure to enable knowledge consumption, including new search paradigms and formats (video, mobile, etc.)? At full maturity, your organizational leadership commits long-term funding to KM and strategic content management.
Take advantage of past improvements by re-using existing services from the current state. At this stage, the capability outlook of the organization is characterized by higher quality and productivity and lower risks. Though activities are pre-defined, successful implementation depends on the individuals involved. Providing informal training ensures individuals are responsible for following a regular pattern to execute the activities.
The initial process is not necessarily a bad stage to be in—all teams have to start somewhere! The main takeaway with this stage is to be aware of the lack of processes and documentation, so you can work with your team to develop them. Level 2 processes are typically repeatable, sometimes with consistent results.
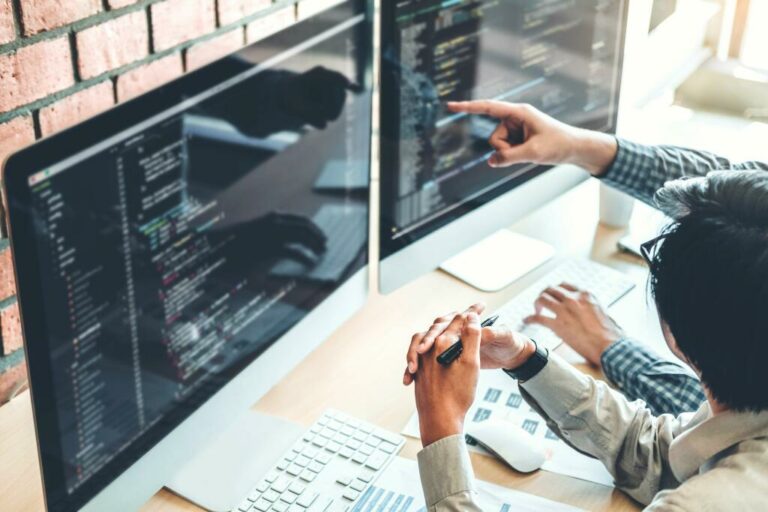

And the expertise to know which activities should be mastered before moving to the next BI maturity level. Data governance is typically siloed around individual enterprise repositories, such as a data warehouse or an Enterprise Resource Planning system. Also, governance is informal, lacking a distinct organizational structure and clearly defined and executed processes. At this stage, some organizations attempt to govern data through enterprise data modeling, which is mostly an academic exercise.
At maturity level 3, processes are managed more proactively using an understanding of the interrelationships of the process activities and detailed measures of the process, its work products, and its services. Defined sets of standard processes are now helping to provide a consistent quality of data to help perform business tasks, meet strategic visions or maintain regulatory compliance. Management and governance oversight has been introduced along with monitoring, alerting and feedback loops. Data inconsistencies have the resources, tools, and funding to be addressed for critical datasets.
The organization, formalization, and management of the practices are not assessed with the capability criteria. This would be part of the governance of practices and therefore assessed as part of the Service Value System maturity. The Capability Maturity Model is a development model created in 1986 after a study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the U.S. The term “maturity” relates to the degree of formality and optimization of processes, from ad hoc practices, to formally defined steps, to managed result metrics, to active optimization of the processes.
Still, Level 2 teams will not yet have learned to live with the dissatisfaction that lab measurements cannot always predict a system’s field behavior. Part of mastery is accepting that the system is complex and must be investigated, rather than fully modeled. Competent managers will begin to look for more general “industry standard” baseline metrics to report against their data. The industry’s default metrics are moving to a better place, but Level 1 managers are unequipped to understand them deeply. They aren’t thinking about the marginal user yet, so even when they do make progress on directionally aligned metrics, nasty surprises can reoccur.
Consistent governance controls across the organization and all ITSM process activities are integrated with the business objectives. Monitoring of appropriate metrics ensures continuous improvement of the organization’s IT capability. But we hope this sheds light on data maturity in 2021, and gives companies direction as they start to become more data mature. Finding how to get CMMI level certification is one of the ways that companies can improve their development processes….
Assurance Services Menu
We outlined the major process areas that could benefit from CMMI in a previous post. If you’d like to have help with your CMMI solution, feel free to contact us at your earliest convenience. Our goal is to help all client businesses be the best that they can https://globalcloudteam.com/ be. At this level, a business can accomplish goals set forward in Levels 2 and 3. Companies who fall into this category can explain what each of their processes do. They are also well-aware of the scope of those processes and the standards they conform to.
To progress from this stage, organizations should focus on building a culture of support for UX at all levels, to gather momentum and move forward across the organization and between projects. Make sure that UX priorities are given due consideration when tradeoffs are made. There’s no official recognition of user experience as a discipline and there are no UX-dedicated roles, processes, or budget. Organizations operating at the fifth IT maturity level can quickly respond to and anticipate change whether working on projects or looking to improve the organization from within.
But the formalized, digital idea of knowledge management that we have today evolved during the early 1990s. Maturity level certificate – Issued for comprehensive assessments including seven or more practices. The number and list of the practices is explicitly stated on the certificate. Is it worth trying to reach Level 3 according to the Richardson maturity model? Level three services lead the service consumers through a trail of resources, causing application state transitions as a result. Maturity level 2 is the most popular usecase of REST principles, which advocate using different verbs based on the HTTP request methods, while the system can have multiple resources.
Maturity Level 1
Organizations often make the costly mistake of undervaluing good project management practices. Gauging project management maturity is especially important for project-based organizations that use projects to perform work. Such organizations include engineering companies, film and video companies, law firms, and marketing and advertising companies. For these companies, leaders may place emphasis on building specialized skills without nurturing project management capabilities. By failing to foster robust project management processes, however, any organization risks financial loss.

What follows is a closer look at this KM maturity model, including how to use it toward enhancing knowledge management maturity within your organization. The ITIL Assessment is conducted by AXELOS Consulting Partners known as ACPs. One method many organizations use to improve themselves is to evaluate their organization against a maturity model and establish a baseline. A maturity model is a reference to a sequential set of capabilities that demonstrates how well an organization is achieving a certain set of practices and capabilities.
Level 5: Strategic Performance #
This isn’t a brand or service success case , but when teams experience different amounts of elasticity in demand vs. performance, it’s always worth trying to understand the user’s context and intent. Nobody goes to work to tank the product, lose revenue, or create problems for others down the line. What separates Level 0 firefighting teams from those that have achieved self-actualised Level 5 execution is not engineering will; it’s context, space, and support. This implies all of the maturity of the previous levels because it requires a situated understanding of which user flows and scenarios are worth automating. This also requires an investment in infrastructure and continuous monitoring.
The Itil Maturity Model
Before we describe the approach, we present our notion of processes which forms basis for the approach. When organizations reach the stage of integrated UX, their UX work has become comprehensive, pervasive, and universal. Almost all teams within the organization usually perform UX-related activities in an efficient, effective manner. There is often innovation in UX methods and processes and even contributions to the field of UX as a whole. The organization’s important success metrics — that leaders care most about — have a focus on UX or are even driven by UX-related work. Capability Maturity Model Integration is an appraisal program administered by the CMMI Institute that assesses the maturity of development processes in a business.
What Is The Benefit Of Knowing Your Project Management Maturity Level?
Sibling teams may not be at the same place, so they educate about the need to treat performance as a commons. Everyone benefits when the commons is healthy, and all areas of the organisation suffer when it regresses. Significant effort is applied to the development and maintenance of custom metrics and tools. Products that do not report RUM data in more sliceable ways (e.g., by percentile, geography, device type, etc.) are discarded for those that better support an investigation. Treating data as a distribution fundamentally enables comparison and experimentation because it creates a language for describing non-binary shifts. Next, firefighting harms teams, and doubly so when management is unwilling to adopt incident response framing.
“The ITIL® maturity model is a tool that organizations can use to objectively and comprehensively assess their service management capabilities and the maturity of the organization’s service value system.” The maturity assessment of the organization’s service value chain component is not focused on the specific value chain model provided in ITIL. Rather, it aims to assess the maturity of the organization’s service value streams, including how they are identified, managed, and improved.
Besides potential acrimony, each incident drains the team’s ability to deliver solutions. Noticeably bad performance is an expression of an existing feature working below spec, and remediation is inherently in conflict with new feature development. Teams can get stuck at Level 1, treating each turn through a Development ➡️ Remediation ➡️ Celebration loop as “the last time”. Upper management will celebrate the first doused fire but will begin to ask questions about the fourth and fifth blazes. Losing an organisation’s confidence is a poor recipe for maximising personal or group potential. Strong Level 1 managers will begin to create dashboards and request reports about factors that have previously caused problems in the product.
When you ask these questions, you can pinpoint what processes you’ll need to focus on to increase your organization’s project management maturity. For example, if you’re currently in level one, you know that the act of creating a project management process is enough to bump you up to the next level. You’re standardizing your project management processes at the team level. Now, you can focus on creating standard practices across the company to promote more cross-functional collaboration. A critical distinction between maturity level 4 and maturity level 5 is the type of process variation addressed.
These are vapid narratives, but Level 0 managers don’t have the situational awareness, experience, or confidence to push back appropriately. They may be passively collecting some data (e.g., through one of the dozens of analytics tools they’ve inevitably integrated over the years), but nobody looks at it. Products that maintain a healthy performance culture elevate management of latency, variance, and other performance attributes to OKRs because they understand how those factors affect the business. Performance is rarely the single determinant of product success, but it can be the margin of victory.
Health data is derived routinely and timely form all key data sources. Data is collected electronically using a variety of tools like spreadsheets, databases and electronic client-based information systems. Data management best practices are in development, but not fully implemented. Some information products are generated, but not routinely, require intensive work and use of resources. Assessment of the five progressive levels of IS4H-MM provides the awareness for planning where to go by Information Systems plans and roadmaps. An ITIL Maturity Assessment provides you the information needed to establish a baseline for your continual improvement needs as well as measure yourself after improvement plans have been implemented.









 0922-03-5678
0922-03-5678